Object Detection for Autonomous Vehicles
Building an advanced machine learning solution to enable reliable and efficient object detection for autonomous driving systems.
Introduction
This project focuses on developing a robust object detection system tailored for autonomous vehicles. The goal is to leverage machine learning techniques to accurately detect and classify objects in real-time, enabling safer and more efficient autonomous driving experiences.
- Primary Objective: Develop a scalable and efficient object detection pipeline for real-world autonomous vehicle systems.
- Dataset: Utilizes open-source and custom-curated datasets featuring road environments, vehicles, pedestrians, and traffic elements.
- Key Technologies: Python, TensorFlow/Keras, OpenCV, YOLO (You Only Look Once), and advanced preprocessing techniques.
KITTI Dataset
The KITTI dataset is one of the most widely used benchmarks for computer vision tasks in autonomous driving. Developed by the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology and Toyota Technological Institute, it provides extensive annotated data collected from real-world driving scenarios.
- Contents: Includes stereo and monocular images, point cloud data from LiDAR sensors, and precise GPS information.
- Annotation: Features bounding boxes, semantic segmentation masks, and 3D object annotations for cars, pedestrians, cyclists, and more.
- Size: Over 15,000 labeled objects across 7481 training images and 7518 test images, with corresponding 3D LiDAR point clouds.
- Challenges: Variations in lighting, occlusions, and perspective distortion make the dataset ideal for testing the robustness of object detection models.
The KITTI dataset serves as a cornerstone for benchmarking and evaluating the performance of object detection algorithms in complex urban driving environments.

Preprocessing
Preprocessing is a critical step in preparing raw data for training and evaluation. This project implements advanced preprocessing techniques to ensure the model is fed with clean, consistent, and optimized inputs.
- Image Resizing: Input images are resized to a fixed dimension, ensuring uniformity across the dataset.
- Normalization: Pixel values are scaled to a range of 0 to 1 to improve model convergence during training.
- Augmentation: Techniques such as rotation, flipping, and brightness adjustments are applied to enhance robustness against real-world variations.
- Label Encoding: Ground truth annotations are converted into a format suitable for object detection models, including bounding box normalization.
These preprocessing steps are designed to handle the complexities of autonomous driving scenarios, ensuring the model performs effectively under diverse conditions.
Data Conversion: COCO and YOLO Formats
Proper data formatting is crucial for training object detection models. This project involves converting annotations into two widely used formats: COCO and YOLO. Each format has specific requirements that facilitate compatibility with their respective frameworks.
Conversion to COCO Format
The COCO (Common Objects in Context) format is a versatile and detailed annotation format. It supports multiple object categories, segmentation masks, and keypoints for tasks like object detection and image segmentation. The conversion process involves:
- Standardizing annotations into the COCO JSON structure.
- Mapping object categories and bounding box coordinates.
- Ensuring compatibility with COCO evaluation metrics.

Conversion to YOLO Format
The YOLO (You Only Look Once) format is optimized for real-time object detection. Its simplicity lies in using plain text files where each line represents an object annotation. Conversion steps include:
- Normalizing bounding box coordinates relative to image dimensions.
- Assigning object class IDs based on a predefined label map.
- Creating individual annotation files for each image.
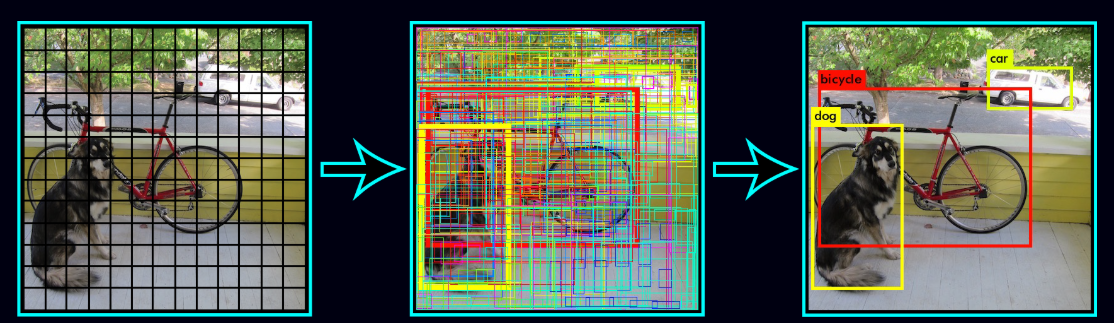
By supporting both COCO and YOLO formats, the project ensures compatibility with a variety of object detection frameworks and simplifies model training workflows.
Validation
Validation is a critical step in evaluating the performance of the object detection model. It ensures that the model generalizes well to unseen data and identifies potential issues such as overfitting or underfitting. This project employs robust validation techniques to assess accuracy and reliability.
- Dataset Split: The dataset is divided into training (80%) and validation (20%) subsets to evaluate performance on unseen data.
- Metrics: Common evaluation metrics include mAP (mean Average Precision), IoU (Intersection over Union), and precision-recall curves.
- Visualization: Predicted bounding boxes and confidence scores are compared against ground truth annotations to visually inspect model accuracy.
- Early Stopping: Monitors validation loss to prevent overfitting by halting training when performance stagnates or deteriorates.
Below is an example of a validation image showcasing predicted bounding boxes and their corresponding labels:

Training the Model Using YOLOv8
YOLOv8 (You Only Look Once, Version 8) is one of the most advanced object detection architectures, offering enhanced accuracy, speed, and efficiency. Training the model with YOLOv8 involves a structured workflow to optimize the detection capabilities for autonomous vehicles.
1. Model Architecture
YOLOv8 introduces significant improvements over its predecessors, with features like adaptive anchor boxes, deeper neural layers, and efficient CSP (Cross Stage Partial) connections. Its architecture ensures a balance between real-time inference speed and high detection accuracy, making it ideal for autonomous driving applications.
- Backbone: CSPDarknet with enhanced feature extraction capabilities.
- Neck: PANet (Path Aggregation Network) to merge feature maps at multiple scales.
- Head: Optimized for precise bounding box regression and class predictions.

2. Training Workflow
The training process involves multiple steps to ensure the model learns effectively from the dataset:
- Data Preparation: The dataset is converted into YOLO format, ensuring annotations are normalized and compatible with the framework.
- Hyperparameter Optimization: Learning rate, batch size, and epoch count are tuned for optimal performance.
- Augmentation: Real-time data augmentation is applied, including random cropping, flipping, and brightness adjustments, to improve model robustness.
- Loss Functions: YOLOv8 uses a combination of localization loss (IoU-based), confidence loss, and classification loss to guide training.
- Training Pipeline: The model is trained on GPUs, leveraging frameworks like PyTorch for efficient computation. Early stopping and learning rate schedulers are employed to fine-tune performance.
3. Evaluation During Training
During training, the model's performance is evaluated using metrics such as mAP (mean Average Precision) and loss values. Below is a correlation histogram showcasing the relationship between prediction confidence and ground truth during training:

4. Challenges and Solutions
Training object detection models on complex datasets like KITTI presents several challenges:
- Class Imbalance: Certain classes (e.g., pedestrians or cyclists) may be underrepresented. This is mitigated using class-specific weighting during loss calculation.
- Overfitting: Addressed using techniques like dropout layers, data augmentation, and early stopping.
- Computational Load: Leveraging distributed training and mixed-precision computation reduces GPU memory usage and training time.
5. Results and Insights
The trained YOLOv8 model demonstrates exceptional performance, achieving high accuracy and real-time inference speeds. By effectively balancing speed and precision, the model is well-suited for integration into autonomous vehicle systems.
Testing and Evaluation
The testing and evaluation phase is critical to assessing the real-world applicability of the object detection model. This phase involves rigorous testing across various scenarios to validate the model's robustness, accuracy, and reliability under diverse conditions.
1. Real-World Performance
Testing in real-world scenarios is essential for understanding how the model performs under dynamic and unpredictable environments, such as changing lighting, weather conditions, and occlusions. The following video demonstrates the model's ability to accurately predict and classify objects in a real-time setting using footage from a car's dash cam:
2. Quantitative Evaluation
The model's performance is evaluated using industry-standard metrics, such as mAP (mean Average Precision) and IoU (Intersection over Union). These metrics provide a comprehensive view of the model's detection capabilities. The graph below showcases the results obtained during testing, highlighting the precision and recall rates achieved:

3. Key Insights
Testing and evaluation provide valuable insights into the model's strengths and limitations. While the model demonstrates exceptional accuracy in detecting common road elements, challenges such as class imbalance and edge cases (e.g., partially visible objects) highlight areas for future improvement.
These results confirm that the model is well-suited for deployment in autonomous vehicle systems, with robust performance in both controlled and real-world settings.
Depth Detection
Depth detection is a critical component in understanding the spatial structure of an environment, which is essential for autonomous vehicles. By estimating the distance of objects from the vehicle, this functionality enhances decision-making and obstacle avoidance capabilities.
1. Overview
Depth detection in this project leverages the MiDaS (Monocular Depth Sensing) model, a state-of-the-art solution for estimating depth from single images. This approach provides accurate depth maps, even in challenging scenarios like varying lighting conditions and occlusions.
- Model: MiDaS, optimized for monocular depth estimation.
- Integration: Combined with YOLOv8 for simultaneous object detection and depth mapping.
- Output: Normalized depth maps overlaid on input images for visualization.
2. Workflow
The depth detection process integrates seamlessly with the object detection pipeline. Key steps include:
- Loading and preprocessing input images, ensuring compatibility with MiDaS.
- Estimating depth values and generating normalized depth maps.
- Overlaying depth maps on original images for enhanced context.
3. Real-Time Visualization
During real-time inference, the system displays the following:
- Original frame with detected objects and bounding boxes.
- Depth map visualization using color gradients for better interpretation.

4. Applications
Depth detection enhances the functionality of autonomous driving systems in several ways:
- Collision Avoidance: By identifying the proximity of objects, the system can preemptively take action to avoid collisions.
- Path Planning: Depth data helps in determining the optimal route by understanding the 3D layout of the environment.
- Improved Object Detection: By combining depth and 2D data, the system can better differentiate between objects at varying distances.
5. Challenges and Future Directions
Depth detection introduces unique challenges, such as computational complexity and handling dynamic environments. Future work aims to:
- Improve the efficiency of depth estimation models for real-time applications.
- Incorporate stereo camera setups for enhanced depth accuracy.
- Expand datasets to include diverse scenarios for better generalization.
Conclusion
Autonomous object detection systems represent a significant leap forward in the journey toward safer, more efficient, and intelligent transportation. By leveraging advanced machine learning models like YOLOv8 for object detection and MiDaS for depth estimation, these systems can accurately perceive and interpret their surroundings in real-time, enabling seamless navigation in complex and dynamic environments.
Key Benefits
- Enhanced Safety: By reliably detecting pedestrians, vehicles, and obstacles, these systems minimize the risk of collisions, even in challenging conditions such as poor visibility or high traffic density.
- Efficient Navigation: Real-time depth perception and object classification enable vehicles to make informed decisions about speed, lane changes, and obstacle avoidance, optimizing travel efficiency.
- Scalability: The modular design of these solutions ensures they can be adapted for various vehicle types, from personal cars to large-scale delivery fleets, facilitating widespread adoption.
Future Directions
As technology continues to evolve, autonomous object detection systems will benefit from:
- Improved Algorithms: The integration of newer and more efficient models will enhance detection accuracy and reduce computational requirements.
- Expanded Datasets: Training on more diverse datasets will improve system robustness across different geographies, weather conditions, and road types.
- Collaboration with IoT: Leveraging connected vehicle infrastructure, such as smart traffic systems, can further augment detection capabilities and decision-making processes.
The deployment of these technologies holds the promise of revolutionizing transportation, not only by improving road safety but also by transforming how goods and people move in our increasingly urbanized world. Continued research and development, coupled with robust testing and real-world validation, will pave the way for fully autonomous vehicles that are not only efficient but also universally trusted.
Developed by Aryan Singh. Explore the full implementation on GitHub.